What Is Uveitis?
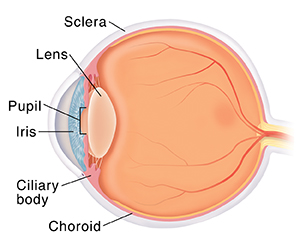
Uveitis is a serious eye problem that can damage your vision. It is inflammation of the uvea. The uvea is the fragile tissue just inside the white outer layer of the eye (the sclera). If you have uveitis, you must see an eye care provider (ophthalmologist) right away. You must get treatment to keep your eyesight. The uvea is made up of 3 parts. Inflammation of any 1 of these is called uveitis:
-
The iris. This is the colored part of the eye and controls the size of the pupil.
-
The ciliary body. This is a muscle attached to the lens of the eye.
-
The choroid. This is located just inside the white of the eye (the sclera). It contains blood vessels to nourish the eye.
What causes uveitis?
Uveitis has many possible causes, including:
In many cases, the cause can’t be found.
How is your eye affected?
Uveitis most often inflames the colored part of your eye (iris). This inflammation is called iritis. The iris opens and closes the pupil. The pupil is the hole through which light enters your eye. Because of this, uveitis can cause pain and sensitivity to light. Often the eye becomes red. Your vision may get blurry. You may see spots floating in your eye. Uveitis can affect one or both eyes. If it is not treated, it can get worse. It can lead to other eye diseases that affect your vision, such as glaucoma or cataracts. It can even cause lasting (permanent) vision loss.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Chris Southard RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Marianne Fraser MSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Melinda Murray Ratini DO
Date Last Reviewed:
3/1/2024
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.