High Blood Pressure and Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Blood pressure measures the force of blood against your artery walls. High blood pressure (hypertension) can harm your arteries. It also puts you at risk for peripheral arterial disease (PAD). PAD is a disease of arteries in the legs that causes poor blood flow. If you have PAD, it’s likely that arteries in other parts of your body are diseased, too. That puts you at high risk for heart attack and other heart diseases.
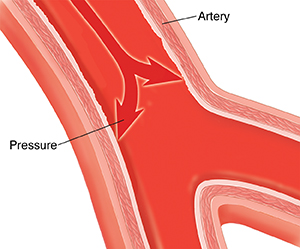
High blood pressure defined
Your blood pressure is too high if it is 130/80 mmHg or higher.
How can high blood pressure lead to peripheral arterial disease?
Having high blood pressure makes it easier for plaque to form. Plaque is a waxy material made up of cholesterol and other things. It can build up in your artery walls. As plaque builds up, your arteries can become narrowed. This limits blood flow. If high blood pressure is not controlled, you are more likely to have PAD and heart problems. But high blood pressure can be controlled with exercise, weight loss, diet changes, and medicine.
What happens if blood pressure isn’t controlled?
You double your risk of dying from heart disease or stroke each time your blood pressure rises:
If you have diabetes, high blood pressure increases your risk for problems from diabetes.
What happens if blood pressure is controlled?
Lowering your blood pressure and keeping it low can reduce your risk for:
-
Stroke
-
Heart attack
-
Dying from heart disease
-
Problems from diabetes
Online Medical Reviewer:
Esther Adler
Online Medical Reviewer:
Mahammad Juber Medical Researcher
Online Medical Reviewer:
Raymond Kent Turley BSN MSN RN
Date Last Reviewed:
9/1/2024
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.