New-Onset Hyperglycemia (Diabetes Suspected)
Your blood sugar is high today. This is called hyperglycemia. It means there is too much sugar (glucose) in your blood.
High blood sugar can have several possible causes, such as:
A common cause is diabetes. Diabetes develops when your body doesn't make enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps control blood sugar. Tests can be done to help find the cause of high blood sugar. To bring your blood sugar down, you may be given insulin.
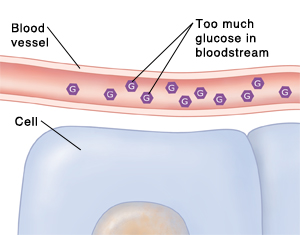
When your body is working normally, the food you eat is digested and turned into sugar. This sugar goes into your bloodstream. Insulin helps sugar move from the blood into the body’s cells. There it is used as fuel. When you have diabetes, the sugar can’t enter the cells. It stays in the blood, causing high blood sugar.
If not controlled, diabetes can cause long-term health problems. Even if you don’t have symptoms, it can harm your blood vessels, heart, nerves, and other organs. Over time, uncontrolled high blood sugar can make a heart attack or stroke more likely.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your healthcare provider as advised. To find out what's causing the high blood sugar, you'll likely need more tests. You'll be told more about these tests. If needed, your provider will refer you to a team that specializes in diabetes care. The diabetes care team can help you learn about and make the changes needed to manage your hyperglycemia. Talk with your provider about starting an exercise program. You may also want to meet with a dietitian. These actions can help control high blood sugar.
When to get medical advice
Call your healthcare provider right away if any of these occur:
When to call 911
Get medical care right away if you have:
-
Chest pain
-
Shortness of breath
-
Confusion
-
Dizziness or lightheadedness
-
Loss of consciousness
-
Weakness of an arm, leg, or 1 side of your face
-
Trouble with speech or vision