Periodontal Disease: Soft Tissue Graft
Gum disease (periodontal disease) is an infection of the gums and tissues that support the teeth. It often gets worse if not treated. Bone damage and tooth loss can occur.
Does your gumline look uneven when you look in the mirror? Or do you see too little gum? These are common effects of gum disease. A type of gum surgery called gingival surgery can lower or even out the gumline. If more of the tooth needs to be exposed, gingival surgery can also fix that. One type of gingival surgery is called a soft tissue graft.
How a soft tissue graft works
The gum can start to pull away when the gum isn't supported by bone. This is called gum recession. Gum recession can be caused by gum disease, injury, and heavy brushing. For a gum graft, healthy tissue can be used to fill in an area where the gum has receded. A graft can be done on one tooth or several teeth. The surgery is done by a periodontist. This is a dentist who specializes in diagnosing and treating gum disease.
-
Before surgery. A gumline that has receded can expose the root. This can make your tooth sensitive. It also lead to cavities in the root. The uneven gumline may also be seen when you smile.
-
During surgery. You will be taken to a procedure room. Your mouth will be numbed so you don't feel pain. The graft tissue may be taken from the roof of your mouth. Or it may be taken from a tissue bank. Tissue may be taken from other gums in your mouth, but that is less common. The tissue will be attached to the area where your gums are receding.
-
After surgery. Graft tissue covers part or all of the exposed root. This protects the root and stops the gum from receding further. It can also improve your appearance. It can reduce tooth sensitivity to touch, heat, cold, and sweet foods. You will go home the same day of your procedure. But you may need an adult to drive you home if you were given a sedative medicine during the procedure. Follow all recovery instructions from your periodontist. These may include:
-
Using a special mouth rinse
-
Taking an antibiotic
-
Eating only soft, cool foods
-
Taking medicine to ease pain
-
Follow-up. Ask the periodontist how you should clean your mouth at home after surgery. Find out when you can brush and floss normally again. You must be careful when cleaning the new graft area until it heals. Be sure to follow up with your periodontist and dentist as instructed.
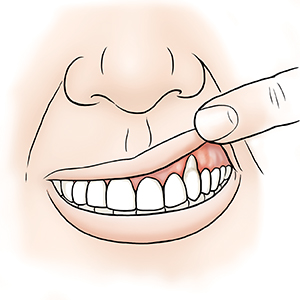 |
| Before surgery. |
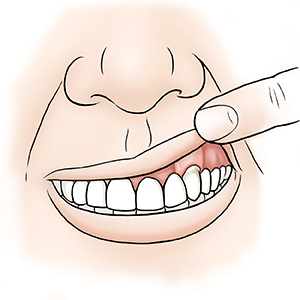 |
| After surgery. |
Online Medical Reviewer:
Jessica Gotwals RN BSN MPH
Online Medical Reviewer:
Michael Kapner MD
Online Medical Reviewer:
Rita Sather RN
Date Last Reviewed:
8/1/2022
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.