When Your Child Needs a Gastrostomy or Gastrojejunostomy Tube
Your child is going home with either a gastrostomy tube (G tube) or gastrojejunostomy tube (G-J tube) in place.
G tube. This is placed through the belly (abdominal) wall into the stomach. This tube sends liquid food directly into the stomach.
G-J tube. This is placed through the abdominal wall into the stomach and leads into the part of the small intestine called the jejunum. It sends liquid food directly into the jejunum.
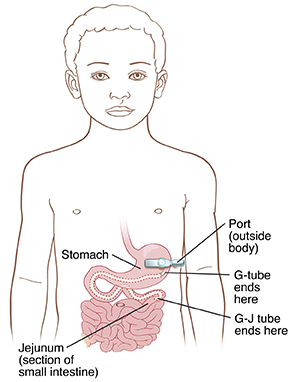 |
| The G-tube or G-J tube is placed so that liquid food or medication is delivered directly into your child’s stomach or small intestine. |
Note
Take care to keep the feeding tube from becoming a strangulation risk to your child. Follow your healthcare team's advice on how to secure the tube safely.
Caring for the G or G-J tube
You will need to care for your child’s tube. You were shown how to do this before your child was discharged from the hospital. For example, you’ll need to flush the tube after feeding or medicine. This is to prevent clogging. And you should know what not to put in the tube, such as whole pills. If you need help, talk with the hospital about how to arrange a home health nurse to help you.
Keep in mind that there are many types of G and G-J tubes, syringes, and feeding pumps. Your child’s tube and supplies may look or work differently from what are described and shown here. Follow the instructions given by your child’s healthcare provider or home health nurse.
Contact information to keep handy
Ask for phone numbers to call if you need help. Also make sure you have the phone number for your child’s medical supply company. You’ll need to order more supplies for your child in the future. Write all of these phone numbers below.
Healthcare provider phone number:
Home health nurse phone number:
Medical supply company phone number:
Feeding your child
You’ll need to feed your child through the tube. You will be shown how to do this before your child is discharged from the hospital. You will also learn how to vent air when needed and to check the balloon if your child’s tube uses a balloon anchor system. If you need more help, talk with the hospital about how to arrange having a home health nurse to help you.
Types of feeding
There are 3 types of feeding with G and G-J tubes. Your child may have one type or a combination of types of feeding. They are:
-
Continuous feeding. Liquid food is dripped slowly through the tube for part or all of a day. Continuous feeding can be done into either the stomach or the jejunum. This type of feeding is only done using a pump. The amount of food to be given and the time frame are often set on the pump for you. Don’t change pump settings unless you’re instructed to do so.
-
Bolus feeding. This is a meal-sized amount of liquid food given through the tube several times a day. Bolus feeding is given using a syringe or a pump. Bolus feeding is done into the stomach but not into the jejunum. Your child’s healthcare provider or home health nurse will tell you how much liquid food to use for each feeding. You’ll also be told how often to feed your child.
-
Gravity feeding. A set amount of formula is placed in a feeding bag. It’s allowed to flow slowly through the tube for at least 30 minutes per feeding.
For bolus feeding, fill in the numbers below:
Feed your child on this schedule:
Give this much at each feeding:
Additional instructions:
When to call the healthcare provider
Call the healthcare provider right away if any of the following occurs:
-
Your child has trouble breathing.
-
The tube feels loose or comes out.
-
The opening where the tube enters the skin becomes larger.
-
Red, rough tissue forms around the tube site.
-
The tube becomes clogged or blocked and you can’t clear it.
-
The skin around the tube site has redness, swelling, leaking fluid, or sores.
-
You see blood around the tube, in your child’s stool, or in the stomach contents.
-
Your child coughs, chokes, or vomits while feeding.
-
Your child’s belly looks bloated or feels hard when gently pressed.
-
Your child has diarrhea or constipation.
-
Your child has a fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as advised by the provider.