Common Spine and Disk Problems
The most common serious back problems happen when disks tear, bulge, or burst open (rupture). In such cases, an injured disk can no longer cushion the vertebrae and absorb shock. As a result, the rest of your spine may also weaken. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and other symptoms.
Torn annulus
A sudden movement may cause a tiny tear in an annulus. Nearby ligaments may stretch.
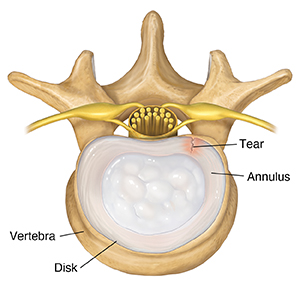 |
| Top view. |
Contained herniated disk
As a disk wears out, the nucleus may bulge into the annulus and press on nerves.
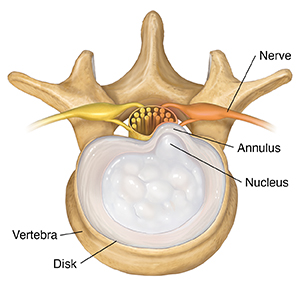 |
| Top view. |
Extruded herniated disk
When a disk ruptures, its nucleus can squeeze out and irritate a nerve.
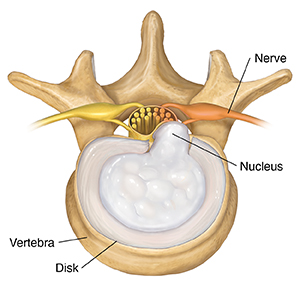 |
| Top view. |
Arthritis
As disks wear out over time, bone spurs form. These growths can irritate nerves and inflame facets.
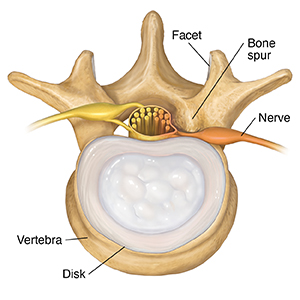 |
| Top view. |
Instability
As a disk stretches, the vertebrae slip back and forth. This can put pressure on the annulus.
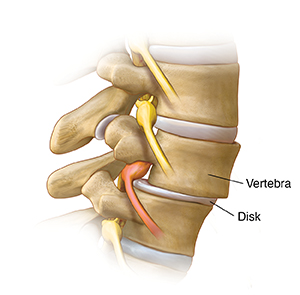 |
| Side view. |
Spondylolisthesis
With this condition, one vertebra has moved forward or backward, in relation to the one above or below it. This causes a crack (stress fracture) in the areas that link the vertebrae together. This may put pressure on the annulus, stretch the disk, and irritate nerves.
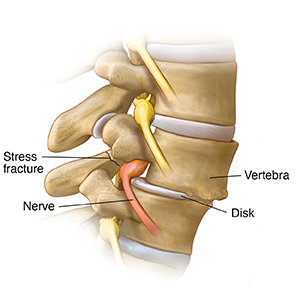 |
| Side view. |
Online Medical Reviewer:
Anne Fetterman RN BSN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Heather M Trevino BSN RNC
Online Medical Reviewer:
Joseph Campellone MD
Date Last Reviewed:
4/1/2024
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.