Stages of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is an infection of the gums and tissues supporting the teeth. If not treated, it often gets worse. Bone damage and tooth loss can occur. Regular self-care and dental visits can help prevent or control periodontal disease.
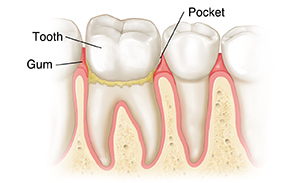
Gingivitis
This is the mildest form of periodontal disease. The gum becomes irritated and swollen (inflamed). The space between the gum and tooth gets deeper, forming a pocket. Gums may become red and may bleed easily. Or you may not have any symptoms. Left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis.
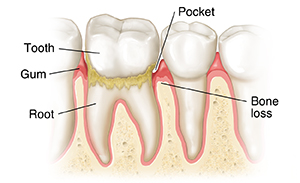
Periodontitis
Infection and inflammation spread to the bone supporting the teeth. Gums may shrink back (recede) from the teeth. Pockets between the teeth can get deeper and harder to clean. You may have bad breath that won't go away. Redness, swelling, and bleeding may develop or get worse. Infection begins to destroy the bone. As bone is destroyed, teeth may start to feel loose.
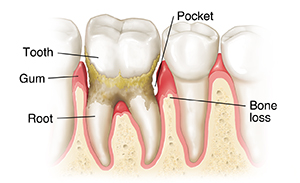
Advanced periodontitis
As periodontitis advances, pockets deepen even more and can fill with pus. Around the roots of the teeth, the gums may start to swell. Bone loss continues. The teeth may feel sensitive to heat or cold and may hurt when brushed. Teeth loosen more. In some cases, teeth may need to be removed to keep the disease from spreading.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Daphne Pierce-Smith RN MSN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Mahammad Juber Medical Researcher
Online Medical Reviewer:
Raymond Turley Jr PA-C
Date Last Reviewed:
2/1/2025
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.